SEO Best Practices for Discontinued Products on Your E-commerce Site
If you're the proprietor of an e-commerce site, you're probably familiar with the challenges of dealing with a vast array of products. However, one area that often gets overlooked is the effective management of discontinued products.
Whether the product is temporarily unavailable or permanently phased out, how you handle these product pages can significantly impact your SEO performance. The best SEO approach for these circumstances heavily depends on whether the discontinuation is temporary or permanent.
Here, we explore both scenarios and provide a comprehensive guide on how to proceed:
Handling Temporarily Discontinued Products
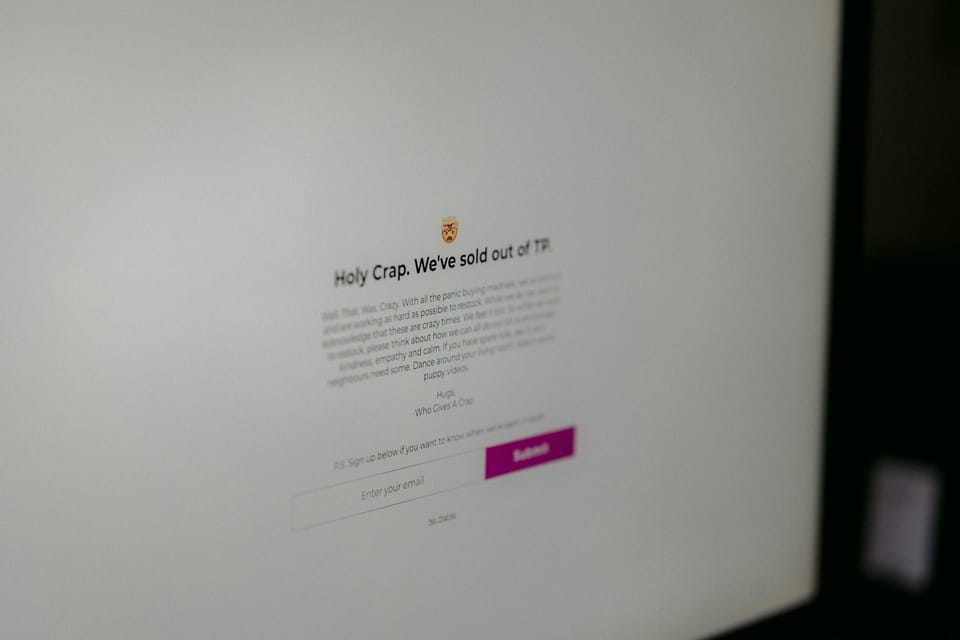
When a product is unavailable but expected to be back in stock in the future, it is crucial to maintain the SEO value of the URL and keep your visitors informed about the product's anticipated return.
In such a case, it's recommended to:
- Keep the page alive: Retain the product page for 2-3 months, preserving its SEO relevance.
- Label as "Out of Stock": Add an "out of stock" to the product image but not in the product details text.
- Hide the Price: Since the product is unavailable, hiding the pricing information is best to prevent confusion.
- Collect Emails: Invite visitors to leave their email addresses so you can notify them when the product is back in stock.
- Maintain the XML Sitemap: Keep the product page in your XML sitemap to ensure search engine crawlers can still find the page.
Dealing with Permanently Discontinued Products
For products that have been permanently discontinued, the approach will differ based on the page's value in terms of organic traffic and external links:
- No Traffic, No Links: If the product page has no traffic or external links, it's best to return an HTTP 410 code to indicate the page no longer exists. Unlike a 404 error, a 410 error helps Google understand that the page is permanently gone.
- Organic Traffic (B): If the product page continues to receive organic traffic, keep it live, but inform users that the product is no longer available. You can also suggest similar products that they might be interested in. When traffic eventually dwindles, remove any internal links pointing to the page, exclude the page from your XML sitemap, apply a 'noindex' directive, and finally, serve an HTTP 410 code.
- External Links (C): If the discontinued product page has a robust backlink profile, consider reusing the URL for another related product, ensuring the content is updated. If a suitable replacement product isn't available, implement a 301 redirect to a relevant product or category page.
Conclusion
Keeping your product pages live is generally more beneficial, even when the products they feature are no longer available. You can maintain customer engagement and preserve your SEO performance by requesting visitor emails, offering alternative products, and providing discount codes for other items.
Remember, each discontinued product presents an opportunity to redirect your visitors' attention to other offerings. With these strategies, you can make the most of these opportunities and keep your SEO robust and healthy.
